How to detect the presence of a species from an environmental sample?
VigiDNA S technologies, based on the “eDNA Barcoding” approach, are mainly used for the monitoring of rare or secretive species in aquatic or terrestrial environments. Those analyses can be performed from water, soil or faecal samples.


Detection of a target species from a water sample
The “eDNA Barcoding” approach for the monitoring of aquatic species has been developed in 2008 by the Laboratoire d’Ecologie Alpine. It is based on the extraction of DNA present in a water sample and its amplification using a specific primer pair for the target species. Scientific studies lead by SPYGEN and its partners have demonstrated that this new method enables improved detection of rare or elusive aquatic species (the detectability depends on the target species) and a reduction in survey costs. It also enables to avoid any risk of introduction of pathogens or invasive species during sampling.
For more information, you can download: Dejean et al. 2012.pdf; Biggs et al. 2015.pdf
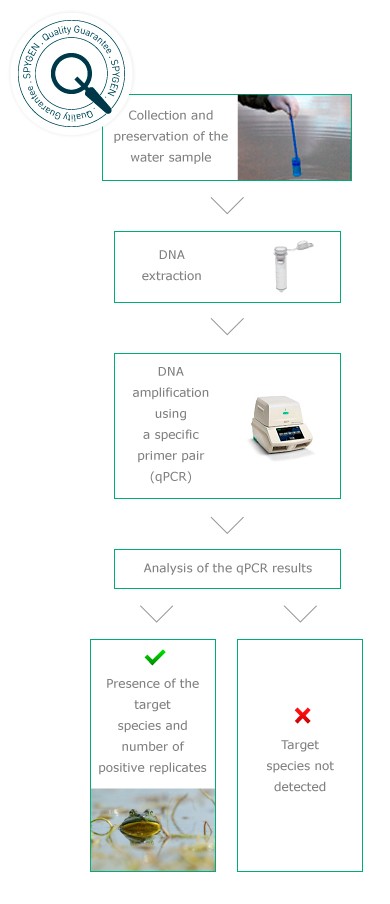
Analyses protocols
-
Quality controls
In order to guarantee the quality of our analyses, controls are performed at each step of the protocol. They enable assessment of the DNA extraction yield, verification of the purity of the consumables used and detection of potential cross-contaminations during the analysis. All specific primer pairs used in the PCR are validated in silico (bioinformatic analyses), in vitro (from tissue samples) and in situ (on sites where the species is known to be present at different densities).

